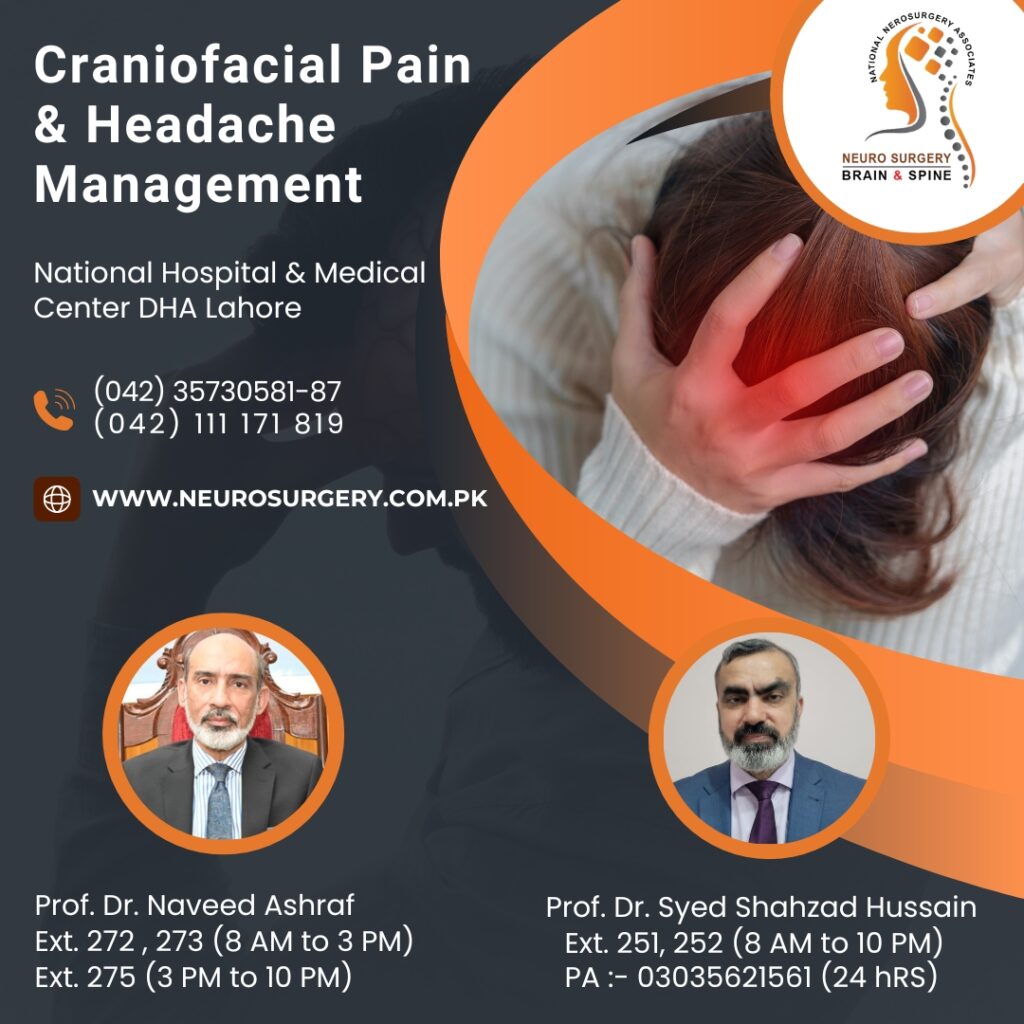
Craniofacial Pain and Headache Management
Headache Management
Headaches are a common medical problem that can range from mild discomfort to severe pain. Proper management depends on identifying the type of headache and its underlying cause.
Types of Headaches
Primary Headaches
Tension Headache
- Most common type
- Often described as a “tight band” around the head
- Triggers by stress, poor posture, or lack of sleep

Migraine
- Moderate to severe throbbing pain, which is mostly progressive, usually on one side but can also be bilateral, involving the whole head.
- May include nausea, vomiting, light/sound sensitivity (photophobia/phonophobia)
- Can have an “aura” (visual disturbances, tingling) before onset
Cluster Headache
- Extremely severe, sharp acute pain around one eye or temple, seen mostly in males.
- Occurs in cyclical patterns (clusters), can have multiple episodes in a day
- May cause tearing, nasal congestion, or restlessness

Secondary Headaches
Tension Headache
- Sinus Headache : (due to sinus infection/inflammation)
- Medication Overuse Headache : (from excessive painkiller use)
- Caffeine Withdrawal Headache
- Post-Traumatic Headache : (after head injury)
- Hypertension-Related Headache : (due to high blood pressure)
- Thunderclap Headache : sudden severe headache secondary to rupture of a brain aneurysm(worst headache of life)
- Meningitis Headache : (severe, with fever and neck stiffness)
- Headache due to Space Occupying lesions in brain : may have insidious onset or acute onset depending upon the nature of SOL. Associated with nausea, vomiting, fits or any neurological deficit.
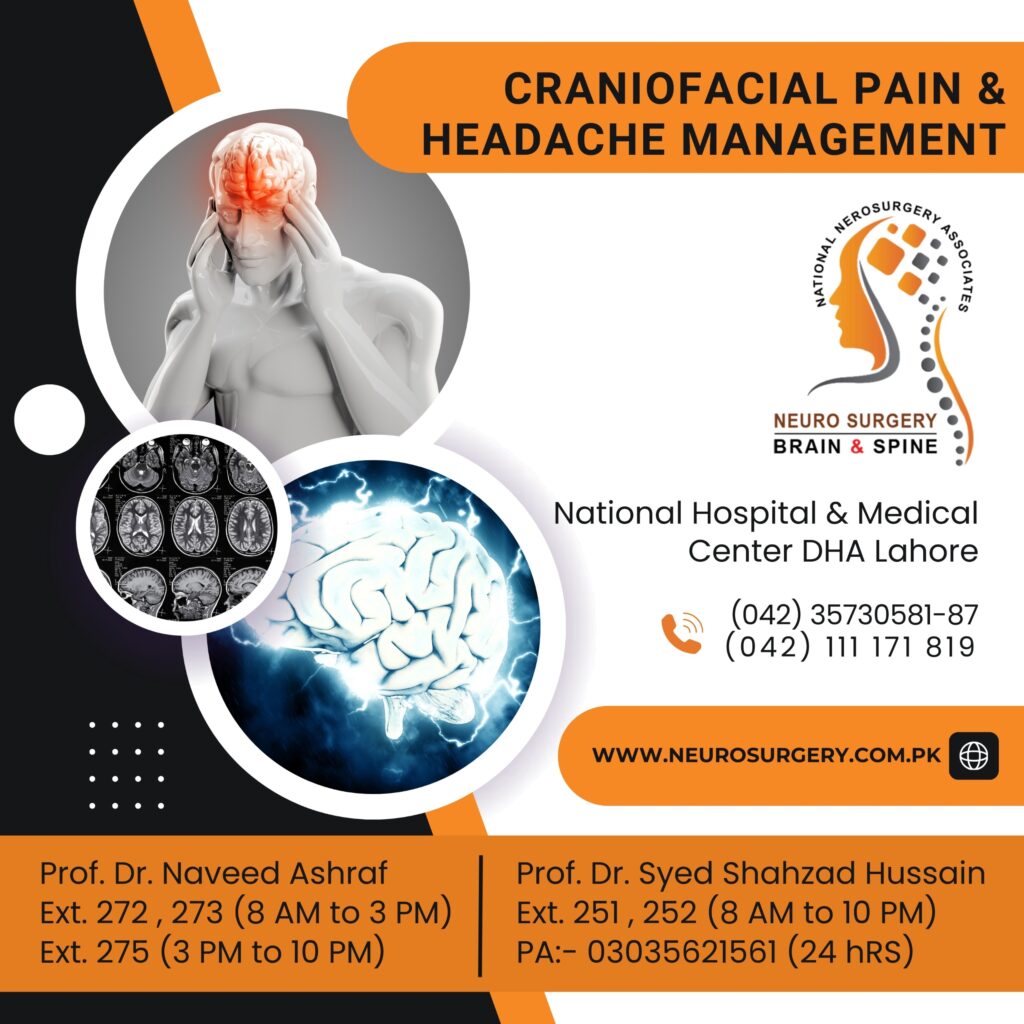
Headache Management
Headaches are a common medical problem that can range from mild discomfort to severe pain. Proper management depends on identifying the type of headache and its underlying cause.
Types and Causes of Craniofacial Pain
1. Neuropathic Pain* (Nerve-related)
Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Sudden, severe, lancinating, electric-shock-like pain in one half of face (along the distribution of trigeminal nerve)
- Triggered by light touch, chewing, or talking
Occipital Neuralgia
- Sharp, stabbing pain at the back of the head (occipital nerve irritation)
- Often caused by neck trauma, infection or muscle tightness
Postherpetic Neuralgia
- Burning pain after a shingles (herpes zoster) outbreak

2. Musculoskeletal Pain
Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ/TMD)
- Jaw pain, clicking, or locking
- Caused by teeth grinding (bruxism), arthritis, or misalignment
Tension-Type Headache
- Dull, band-like pain around the head and face
- Often due to stress, poor posture, or muscle strain
3. Vascular Pain
Migraine with Facial Involvement
- Throbbing pain extending to the cheek, jaw, or eye
- May include nausea, light sensitivity
Cluster Headache
- Severe, stabbing pain around one eye, often with tearing/nasal congestion
4. Sinus and Dental Pain
Sinusitis
- Pressure-like pain in cheeks/forehead, worsens with bending forward
Dental Causes
- Tooth abscess, cavities, or impacted wisdom teeth
5. Atypical Facial Pain
- Chronic, poorly localized pain without a clear structural cause
- Often linked to psychological factors (stress, depression)
Management of Craniofacial Pain
1. Pharmacological Treatment
Neuropathic Pain
- Anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Gabapentin, Pregabalin)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline)
- Nerve blocks (lidocaine, steroids)
Vascular Pain (Migraine/Cluster)
- Triptans (Sumatriptan)
- CGRP inhibitors (for chronic migraines)
- Oxygen therapy (for cluster headaches)
2. Non-Pharmacological Approaches
- Physical Therapy* (For TMJ, neck-related pain)
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Stress reduction
- Avoiding triggers (certain foods like cheese, chocolates,alcohol, caffeine)
- Proper sleep and hydration
3. Interventional & Surgical Options
- Nerve Blocks* (For trigeminal/occipital neuralgia)
- Radiofrequency Ablation
- Microvascular Decompression* (For trigeminal neuralgia due to blood vessel compression/vascular conflict on Trigaminal nerve